A research team led by Professor Jui-I Chao from the Department of Biological Science and Technology at the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University (NYCU) recently discovered that the autophagy receptor sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1)/p62 molecule plays a crucial role in nanodrug delivery and the effectiveness of cancer treatment. This finding is instrumental in improving the efficacy of nanodrugs, developing new drugs to overcome drug resistance, and bringing hope to cancer patients undergoing nanodrug therapy.
Unlocking the Potential: SQSTM1 Identified as Crucial in Nanodrug Delivery for Cancer Treatment
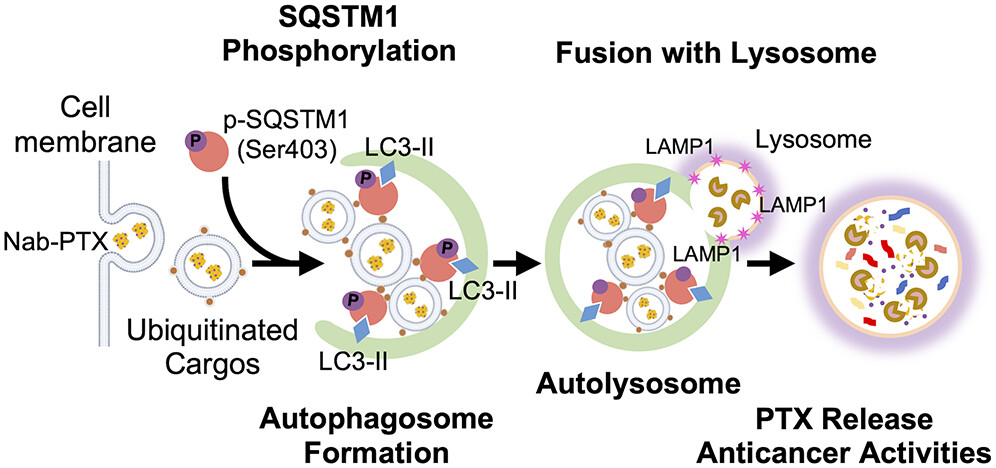
Cancer poses a significant challenge in the global health arena, and nanodrug therapy is considered a potential breakthrough in treatment. The SQSTM1 protein can regulate the transport, breakdown, and metabolism of nanoparticles and nanodrugs within cells, influencing drug efficacy. Therefore, it is considered a key molecule in nanoparticulophagy.
On October 31st, NYCU announced that Prof. Jui-I Chao’s research team identified SQSTM1 as a critical factor in nanodrug delivery and the effectiveness of cancer treatment, particularly in the action of albumin nanodrugs on cancer cells. This discovery can promote the release of nanodrugs and enhance their anti-cancer activity. This significant research finding lays the foundation for delivering and treating cancer using albumin nanodrugs, opening up new avenues for research and innovative therapies in nanoparticulophagy in cancer.
The study found that the protein regions and phosphorylation of SQSTM1 play a crucial role in nanoparticulosome formation and nanoparticulophagy. Additionally, the research team observed high expression of SQSTM1 in cancer cells of clinical patients with lung, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer, making SQSTM1 an essential target for nanodrug delivery and cancer treatment.
Innovative Treatment on the Horizon: Development of Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel (Nab-PTX) by Prof. Jui-I Chao’s Research Team
Prof. Jui-I Chao pointed out that understanding the molecular mechanisms and targeting molecules of nano-autophagy helps elucidate the role of clinical albumin nanodrugs, improves the efficacy of nanodrugs, and leads to significant breakthroughs in developing new drugs to overcome drug resistance. This research also provides new strategies for the treatment of other diseases.
NYCU stated that the research received long-term support from the National Science and Technology Council Program, the Ministry of Education’s Higher Education Sprout Project, and the NYCU Center for Intelligent Drug Systems and Smart Bio-devices. The research results were published in the prestigious academic journal ACS Nano.
Additionally, NYCU mentioned that Prof. Jui-I Chao’s research team is now developing a new type of albumin-bound paclitaxel (Nab-PTX) drug, expected to be more effective against cancer cells than clinically used Nab-PTX drugs. The research results are anticipated to contribute significantly to the treatment of clinical cancer patients.