Chi-Hung Lin, President
Haydn Chen, Chief Strategy Officer
National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
February 2023
Nurturing talents is the primary responsibility of a university and talents are the assets to the society for they are the ones to define, create, enrich, sustain or tarnish the future of all human living on earth. It behooves all of us working in higher education, as well those in the primary and secondary education, to design curriculum with updated composition and content that would facilitate the young minds to learn knowledge, skills, creativity, ethics, empathy, communication, team spirit so they can contribute valuably to the society and fulfill their civil responsibilities. As teachers we must not lose sight of being the mentors of and the providers of knowledge to the students; we must keep pace with the advancement of technology and social-economics so to prepare ourselves first before we can confidently educate students with right set of learning environment and pedagogy in order to empower them to reach their full capacities. One example is the recent hot topic of ChatGPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), should this tool be ignored, forbidden, or should it be encouraged or even embraced in teaching and learning? Irrespective of the answers to the above question, teachers must have the mindset of being receptive to changes, being global, stimulating, forward-thinking, and human-centric in the creation, preservation and transfer of knowledge to the next generation.
According to the future trend of employment market driven by six forces1 and following the guidelines for high education policies in the MOE’s SPROUT2 project of Taiwan, the newly merged National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University (NYCU) embarks on a new education philosophy to nurture future talents. NYCU is mindful of the current status and future trend in higher education, which includes the local factors such as low birth rate and high demand for high-tech employees and the global emphasis on digital transformation, new technology, international mobility and sustainable development; hence, guiding the university leaders to reflect and redesign the curriculum and teaching methods. After researching the ways and means that other world leading universities have taken to face the future challenges NYCU positions herself to design her own model for higher education – the NYCU Model.
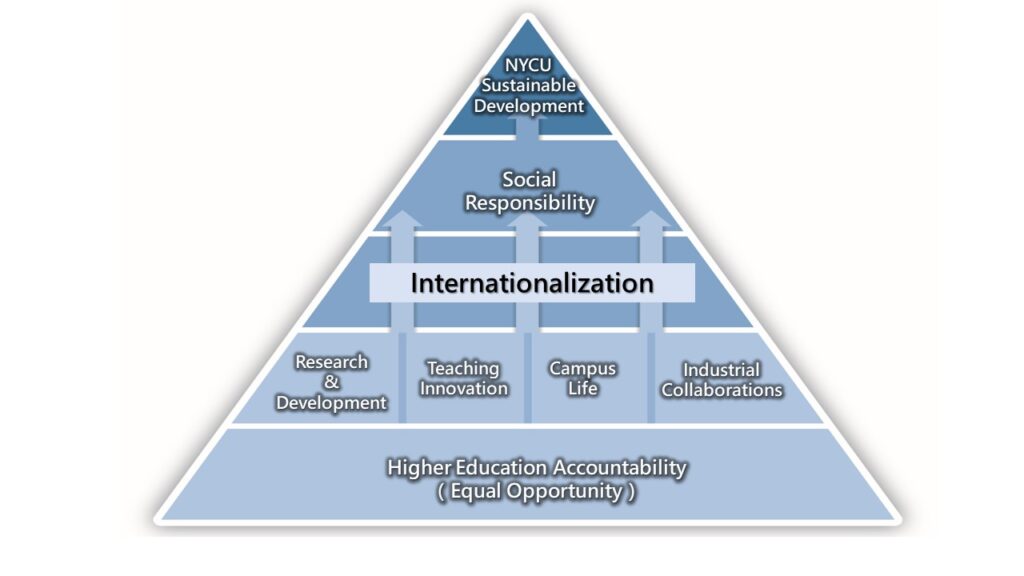
The NYCU Model of higher education is depicted in the pyramid structure shown in Figure 1, in which the ultimate goal of the education is aimed to reaching the sustainability on all aspects of the university operation and functions. Being a public university NYCU carries the mission to serve all people who are able and willing to attend tertiary education with diversity, equal opportunity and inclusiveness; moreover the university must be accountable. On such a foundation there are four pillars supporting the NYCU education; they are “Teaching Innovation”, “Campus Life”, “Research & Development” and “Industrial Collaborations”. Via classroom teaching, living and learning on campus, together with research and industrial collaborations, NYCU is committed to educating students with disciplinary specialty as well as liberal arts learning to assure that both hard skills and soft skills, so critically required for future employees, are learned. The four pillars of education must then be connected via internationalization that encompasses localized learning of global issues and international outreach to people, matters and issues in the world. Thereafter the university social responsibility must be deeply embedded in the mind of the students for they are the masters for the future.
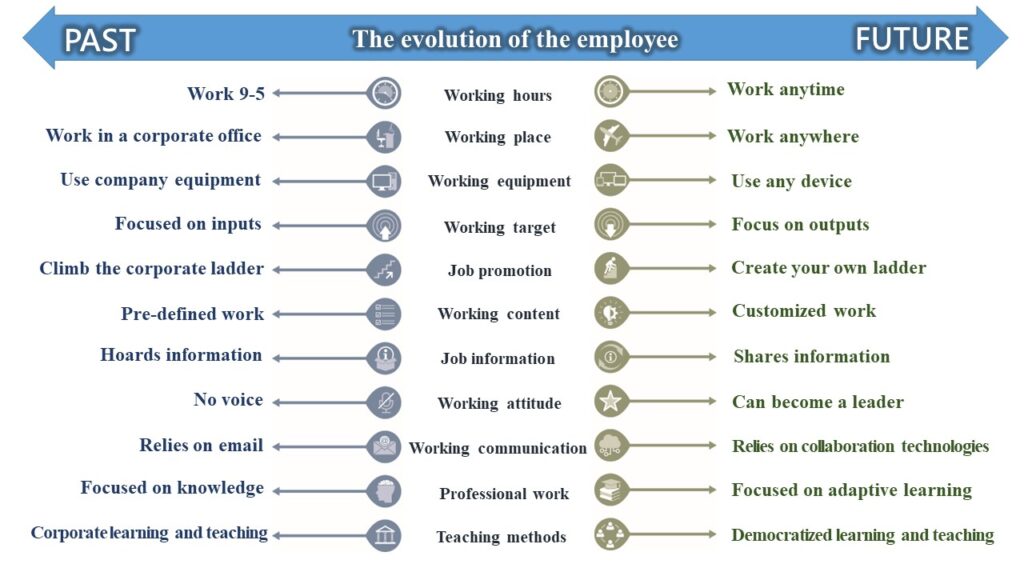
A comparison of the working style and culture between the past and the future employees can be found in Figure 2 where the evolution of the employee casts a different perception and direction for the future workers. As such, a university must prepare students to become thinkers and doers with the forward-looking mindset and innovative ideas and creative mind.
The future trend of teaching must be converted from one way dissemination of knowledge to more dynamic and diversified approaches that would grasp the attention of students and be more engagingly interactive. Students also need to bear their own responsibilities by being a self-learner, an adaptive learner and more importantly, a lifelong learner. The common belief amongst the leaders of the world higher education institutes is that the future university will be composed of elements that fall into three main categories: degree composition, teaching methodology, cultivating soft skills. Figure 3 describes the guiding principles for the positioning of future universities following the above three categories. Each university in any given country has different set of laws and culture along with different visions and missions, so the positioning of a university for the future must be tailored made as no one simple model can be applied to all universities.
Degree Composition: Flexibility is given to learners with many options to acquire cross-domain knowledge and lifelong learning opportunity.
Teaching Methodology: Blended learning, adaptive learning, practices, problem-based learning, mission-driven learning are all possible.
Cultivating Soft Skills: The ever increasing importance of soft skills as shown in Fig. 3 must be nurtured in common courses, general education, and campus life.

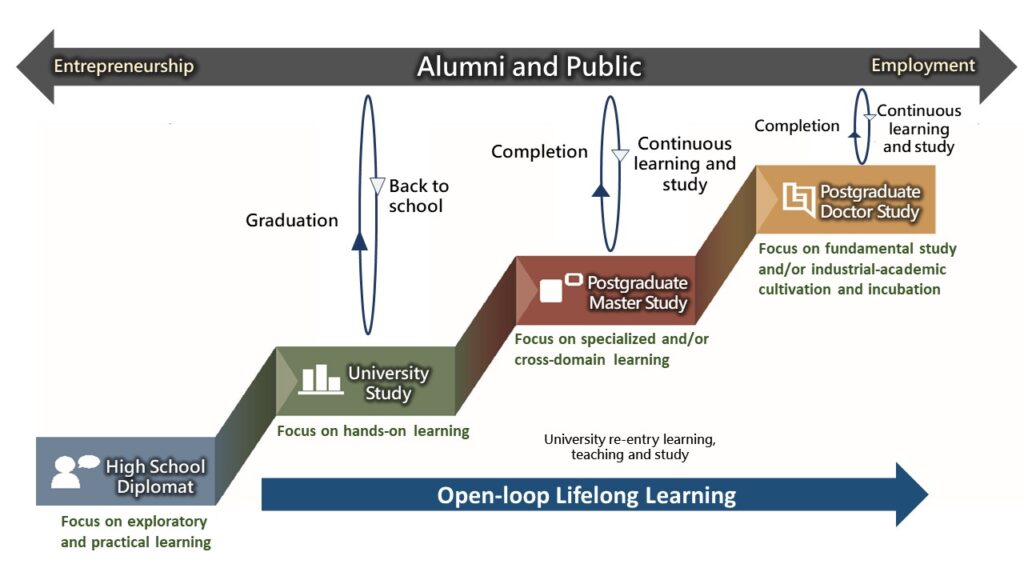
In light of the above description for the future university the NYCU Model has taken on the following strategy to create a learning community for all students from high school graduates to the alumni and public. A lifelong learning map detailing the various pathways for all people to continuously learn and study over their entire lives is presented in Figure 4.
Besides a traditional pathway for high school graduates to attend University for their degrees, non-traditional students are given opportunities to return back to university to study new subject and/or advanced degrees. Continuous learning and study are the key to lifelong learning, be it for a postgraduate degree or simply for new interest. This Open-loop model allows alumni and the public to return to NYCU that provides an excellent learning environment with modern facilities, updated subjects, outstanding teachers and industrial connections.
It can be seen in Fig. 4 that the main focus for each degree-seeking student at the undergraduate, master and doctor level is different. While education of a bachelor degree student is focused on hand-on learning of practices, postgraduate students will have their focus on fundamental studies and/or cross-domain specialty learning as well as industrial collaborations. Innovation and entrepreneurship are also components of study if they so choose.
The NYCU Model of higher education is to combine the market needs, the advancement of technology as well as the pursuit of new adventure in lifelong learning. It is designed to enrich students of all ages with knowledge and skills that would help their professional career and/or their individual interests so that all can have a happy, engaging, fulfilling and satisfying life.
- Based upon a publication by the Institute for the Future (IFTF) of the University of Phoenix in 2011, following six driving forces are identified to change the future job market: 1) aging society with improving health care, 2) smart machines and system, 3) data analytics with mass information, 4) new media ecology, 5) super large organization, 6) global connection.
- The Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan has launched a SPROUT (Sustain Progress and the Rise of University of Taiwan) project from 2018 onwards to support teaching, research, services and university social responsibility, etc. It is on a competitive basis for the first phase spanning from 2018-2022. The second phase proposals are currently under review.
